p53 DBD N-terminaly truncated p53 DBD
Notre recherche
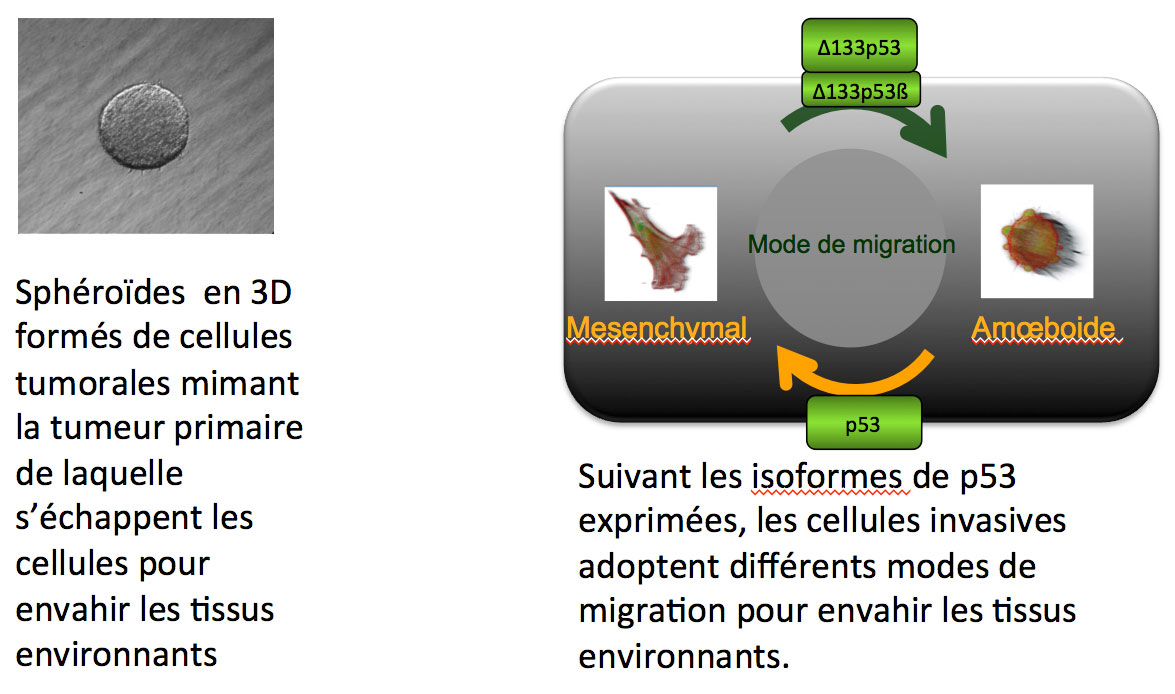
Les cellules d’un organisme ont la capacité de se déplacer. Mais pas n’importe comment. Ce processus fondamental obéit à des régulations strictes essentielles à certains traits de vie, par exemple le développement embryonnaire ou la mise en action des défenses immunitaires. Mal contrôlée, la migration cellulaire provoque des pathologies graves telles que la formation de métastases, résultant d’une dissémination des cellules cancéreuses à partir de la tumeur primaire et entraînant à échéance la mort. Comprendre comment une cellule cancéreuse devient invasive et identifier les processus moléculaires qui règlent cette migration anormale sont des questions biologiques primordiales et constituent notre domaine de recherche.
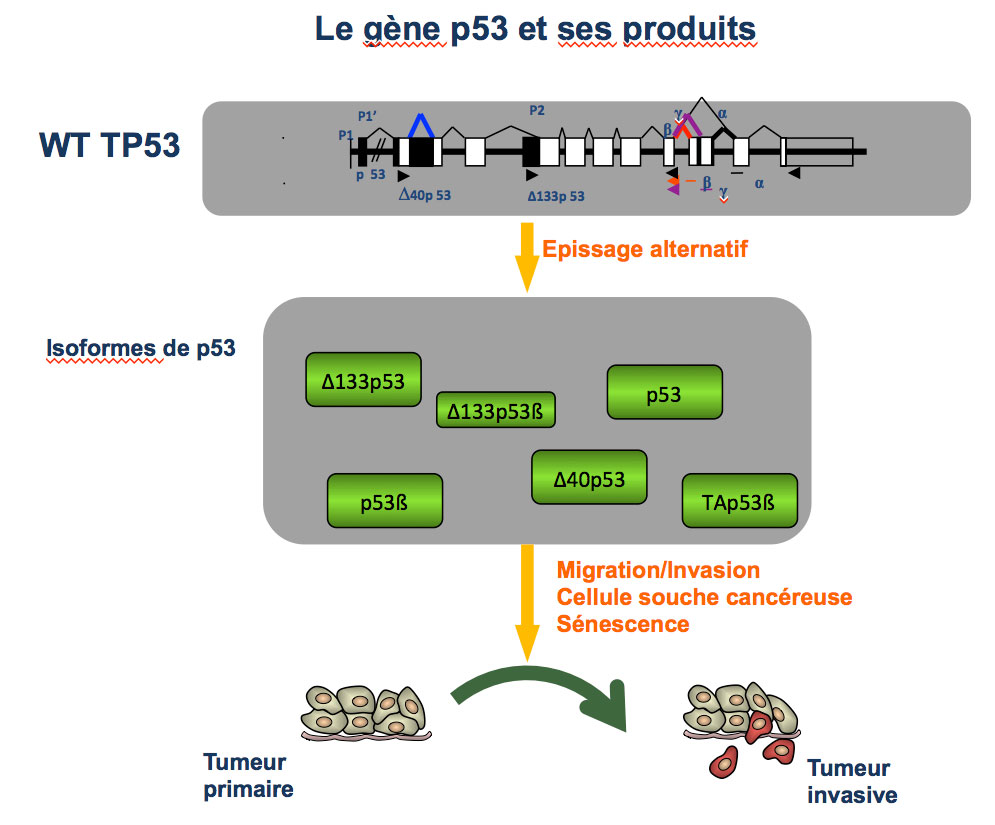
Le suppresseur de tumeurs p53 est le gène plus souvent muté dans les tumeurs humaines et le sujet de nombreux travaux. Nos études sont focalisées sur les mécanismes utilisés par la cellule tumorale pour inactiver la fonction de p53. Malgré l’immense prévalence de p53 dans la progression des tumeurs humaines, il apparaît aujourd’hui que les mutations qui affectent le gène p53 (TP53) ne peuvent pas expliquer précisément l’acquisition d’un phénotype invasif. Ainsi, de nombreuses données cliniques montrent que le statut mutationnel de p53 ne peut pas être utilisé comme un marqueur pronostique de la progression tumorale, indiquant que d’autres mécanismes de régulation du gène permettent d’inactiver sa fonction suppresseur de tumeurs.
Un des mécanismes est la production de protéines variantes (isoformes) par épissage alternatif du gène – un processus contrôlant la présence ou l’absence de certains domaines protéiques. Notre équipe étudie les isoformes produites par les cellules cancéreuses, les mécanismes moléculaires sous-jacents et leurs conséquences sur l’invasion métastatique.
Nous analysons le rôle des isoformes de p53 dans des processus cellulaires associées à l’invasion tumorale : le mode de migration, la sénescence cellulaire et la formation de cellules souches tumorales. Un objectif majeur est de déterminer si certaines isoformes sont associées à l’agressivité tumorale et constituent de nouvelles cibles thérapeutiques. Dans cette optique, nous souhaitons identifier les programmes cellulaires qui contrôlent l’expression des isoformes de p53 lors de l’invasion cancéreuse et décoder les mécanismes par lesquels ces isoformes contrôlent l’invasion cancéreuse grâce à l’identification de leurs partenaires et de leurs cibles.
Nos études in vivo sont réalisées dans des cellules cultivées en 2D, mais également en 3D pour se rapprocher des conditions physiologiques des tissus. Nous combinons les analyses cellulaires (potentiel de cellule souche, vidéomicroscopie de cellules vivantes et xénogreffes murine) à l’analyse de tumeurs humaines et les analyses protéomique et transcriptomique à haut débit.
En savoir plus
Financements

Publications
2022
- Reciprocal regulation of p21 and Chk1 controls the cyclin D1-RB pathway to mediate senescence onset after G2 arrest. Lossaint G, Horvat A, Gire V, Bačević K, Mrouj K, Charrier-Savournin F, Georget V, Fisher D, Dulić V. J Cell Sci. 2022 Apr 15;135(8):jcs259114. Pubmed
- Regulation of Src tumor activity by its N-terminal intrinsically disordered region. Aponte E, Lafitte M, Sirvent A, Simon V, Barbery M, Fourgous E, Boublik Y, Maffei M, Armand F, Hamelin R, Pannequin J, Fort P, Pons M, Roche S. Oncogene. 2022 Feb;41(7):960-970. Pubmed
2021
- Mechanisms and Regulation of Cellular Senescence. Roger L, Tomas F, Gire V. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 6;22(23):13173 Pubmed
- NOPCHAP1 is a PAQosome cofactor that helps loading NOP58 on RUVBL1/2 during box C/D snoRNP biogenesis. Abel Y, Paiva ACF, Bizarro J, Chagot ME, Santo PE, Robert MC, Quinternet M, Vandermoere F, Sousa PMF, Fort P, Charpentier B, Manival X, Bandeiras TM, Bertrand E, Verheggen C. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 25;49(2):1094-1113 Pubmed
- Dependent Oncogenic Signaling of the PEAK3 Pseudo-Kinase. Ounoughene Y, Fourgous E, Boublik Y, Saland E, Guiraud N, Recher C, Urbach S, Fort P, Sarry JE, Fesquet D, Roche S. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 17;13(24):6344 Pubmed
- Aspartate-phobia of thermophiles as a reaction to deleterious chemical transformations. Villain E, Fort P, Kajava AV. Bioessays. 2022 Jan;44(1):e2100213 Pubmed
- Δ133p53β isoform pro-invasive activity is regulated through an aggregation-dependent mechanism in cancer cells. Arsic N, Slatter T, Gadea G, Villain E, Fournet A, Kazantseva M, Allemand F, Sibille N, Seveno M, de Rossi S, Mehta S, Urbach S, Bourdon JC, Bernado P, Kajava AV, Braithwaite A, Roux P. Nat Commun 12:5463 Pubmed
- p53, A Victim of the Prion Fashion. Billant O, Friocourt G, Roux P, Voisset C. Cancers (Basel). 13(2):269 Pubmed
2019
- New insights into the evolutionary conservation of the sole PIKK pseudokinase Tra1/TRRAP. Elías-Villalobos A, Fort P, Helmlinger D. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Dec 20;47(6):1597-1608 Pubmed
- The atypical RhoU/Wrch1 Rho GTPase controls cell proliferation and apoptosis in the gut epithelium. Slaymi C, Vignal E, Crès G, Roux P, Blangy A, Raynaud P, Fort P. Biol Cell. 2019 May;111(5):121-141 Pubmed
2018
- PIP30/FAM192A is a novel regulator of the nuclear proteasome activator PA28γ. Jonik-Nowak B, Menneteau T, Fesquet D, Baldin V, Bonne-Andrea C, Méchali F, Fabre B, Boisguerin P, de Rossi S, Henriquet C, Pugnière M, Ducoux-Petit M, Burlet-Schiltz O, Lamond AI, Fort P, Boulon S, Bousquet MP, Coux O. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. pii: 201722299. Pubmed
- SOX9 has distinct regulatory roles in alternative splicing and transcription. Girardot M, Bayet E, Maurin J, Fort P, Roux P, Raynaud P. Nucleic Acids Res. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky553. Pubmed
- The RPAP3-Cterminal domain identifies R2TP-like quaternary chaperones. Maurizy C, Quinternet M, Abel Y, Verheggen C, Santo PE, Bourguet M, C F Paiva A, Bragantini B, Chagot ME, Robert MC, Abeza C, Fabre P, Fort P, Vandermoere F, M F Sousa P, Rain JC, Charpentier B, Cianférani S, Bandeiras TM, Pradet-Balade B, Manival X, Bertrand E. Nat Commun. 9(1):2093. Pubmed
- ∆133p53 isoform promotes tumour invasion and metastasis via interleukin-6 activation of JAK-STAT and RhoA-ROCK signalling. Campbell H, Fleming N, Roth I, Mehta S, Wiles A, Williams G, Vennin C, Arsic N, Parkin A, Pajic M, Munro F, McNoe L, Black M, McCall J, Slatter TL, Timpson P, Reddel R, Roux P, Print C, Baird MA, Braithwaite AW. Nat Commun. 9(1):254. Pubmed
2017
- The Evolutionary Landscape of Dbl-Like RhoGEF Families: Adapting Eukaryotic Cells to Environmental Signals. Fort P, Blangy A. Genome Biol Evol. 9:1471-1486. Pubmed
- Heterogeneity in sarcoma cell lines reveals enhanced motility of tetraploid versus diploid cells. Jemaà M, Abdallah S, Lledo G, Perrot G, Lesluyes T, Teyssier C, Roux P, van Dijk J, Chibon F, Abrieu A, Morin N. 14291 Pubmed
- Binding site density enables paralog-specific activity of SLM2 and Sam68 proteins in Neurexin2 AS4 splicing control. Danilenko M, Dalgliesh C, Pagliarini V, Naro C, Ehrmann I, Feracci M, Kheirollahi-Chadegani M, Tyson-Capper A, Clowry GJ, Fort P, Dominguez C, Sette C, Elliott DJ. Nucleic Acids Res. pii: gkw1277. Pubmed
- The p53 isoform delta133p53ß regulates cancer cell apoptosis in a RhoB-dependent manner. Arsic N, Ho-Pun-Cheung A, Evelyne C, Assenat E, Jarlier M, Anguille C, Colard M, Pezet M, Roux P, Gadea G. PLoS One. 12:e0172125. Pubmed
2016
- TP53 drives invasion through expression of its Δ133p53β variant. Gadea G, Arsic N, Fernandes K, Diot A, Joruiz SM, Abdallah S, Meuray V, Vinot S, Anguille C, Remenyi J, Khoury MP, Quinlan PR, Purdie CA, Jordan LB, Fuller-Pace FV, de Toledo M, Cren M, Thompson AM, Bourdon JC, Roux P. 5: e14734. Pubmed
- A SLM2 Feedback Pathway Controls Cortical Network Activity and Mouse Behavior. Ehrmann I, Gazzara MR, Pagliarini V, Dalgliesh C, Kheirollahi-Chadegani M, Xu Y, Cesari E, Danilenko M, Maclennan M, Lowdon K, Vogel T, Keskivali-Bond P, Wells S, Cater H, Fort P, Santibanez-Koref M, Middei S, Sette C, Clowry GJ, Barash Y, Cunningham MO, Elliott DJ. Cell Rep. 17:3269-3280. Pubmed
- STARs in the CNS. Ehrmann I, Fort P, Elliott DJ. Biochem Soc Trans. 44:1066-72. Pubmed
- High chlorpyrifos resistance in Culex pipiens mosquitoes: strong synergy between resistance genes. Alout H, Labbé P, Berthomieu A, Makoundou P, Fort P, Pasteur N, Weill M. Heredity (Edinb). 116:224-31. Pubmed
2015
- Greatwall promotes cell transformation by hyperactivating AKT in human malignancies. Vera J, Lartigue L, Vigneron S, Gadea G, Gire V, Del Rio M, Soubeyran I, Chibon F, Lorca T, Castro A. 4:e10115. Pubmed
- Neural differentiation modulates the vertebrate brain specific splicing program. Madgwick A, Fort P, Hanson PS, Thibault P, Gaudreau MC, Lutfalla G, Möröy T, Abou Elela S, Chaudhry B, Elliott DJ, Morris CM, Venables JP. PLoS One. 10:e0125998. Pubmed
- Senescence from G2 arrest, revisited. Gire V, Dulic V. Cell Cycle. 14:297-304. Pubmed
- Evolution of proteasome regulators in eukaryotes. Fort P, Kajava AV, Delsuc F, Coux O. Genome Biol Evol. 7:1363-79. Pubmed
- Atypical RhoV and RhoU GTPases control development of the neural crest. Faure S, Fort P. Small GTPases. 6:174-7. Pubmed
- Stable coexistence of incompatible Wolbachia along a narrow contact zone in mosquito field populations. Atyame CM, Labbé P, Rousset F, Beji M, Makoundou P, Duron O, Dumas E, Pasteur N, Bouattour A, Fort P, Weill M. Mol Ecol. 24:508-21. Pubmed
- The p53 isoform Δ133p53β promotes cancer stem cell potential. Arsic N, Gadea G, Lagerqvist EL, Busson M, Cahuzac N, Brock C, Hollande F, Gire V, Pannequin J, Roux P. Stem Cell Reports. 4:531-40. Pubmed
2014
- Postprandial triglyceride-rich lipoproteins promote invasion of human coronary artery smooth muscle cells in a fatty-acid manner through PI3k-Rac1-JNK signaling. Varela LM, Bermúdez B, Ortega-Gómez A, López S, Sánchez R, Villar J, Anguille C, Muriana FJ, Roux P, Abia R. Mol Nutr Food Res. 58:1349-64. Pubmed
- Antagonistic functions of LMNA isoforms in energy expenditure and lifespan. Lopez-Mejia IC, de Toledo M, Chavey C, Lapasset L, Cavelier P, Lopez-Herrera C, Chebli K, Fort P, Beranger G, Fajas L, Amri EZ, Casas F, Tazi J. EMBO Rep. 15:529-39 Pubmed
- PleiotRHOpic: Rho pathways are essential for all stages of Neural Crest development. Fort P, Théveneau E. Small GTPases. 5:e27975. Pubmed
- Wolbachia divergence and the evolution of cytoplasmic incompatibility in Culex pipiens. Atyame CM, Labbé P, Dumas E, Milesi P, Charlat S, Fort P, Weill M. PLoS One. 9:e87336. Pubmed
2013
- The tissue-specific RNA binding protein T-STAR controls regional splicing patterns of neurexin pre-mRNAs in the brain. Ehrmann I, Dalgliesh C, Liu Y, Danilenko M, Crosier M, Overman L, Arthur HM, Lindsay S, Clowry GJ, Venables JP, Fort P, Elliott DJ. PLoS Genet. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003474. Pubmed
- Applying ecological and evolutionary theory to cancer: a long and winding road. Thomas F, Fisher D, Fort P, Marie JP, Daoust S, Roche B, Grunau C, Cosseau C, Mitta G, Baghdiguian S, Rousset F, Lassus P, Assenat E, Grégoire D, Missé D, Lorz A, Billy F, Vainchenker W, Delhommeau F, Koscielny S, Itzykson R, Tang R, Fava F, Ballesta A, Lepoutre T, Krasinska L, Dulic V, Raynaud P, Blache P, Quittau-Prevostel C, Vignal E, Trauchessec H, Perthame B, Clairambault J, Volpert V, Solary E, Hibner U, Hochberg ME. Evol Appl. 2013 Jan;6(1):1-10. Pubmed
- Eroded human telomeres are more prone to remain uncapped and to trigger a G2 checkpoint response. Jullien L, Mestre M, Roux P, Gire V. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(2):900-11. Pubmed
- MBNL1 and RBFOX2 cooperate to establish a splicing programme involved in pluripotent stem cell differentiation. Venables JP, Lapasset L, Gadea G, Fort P, Klinck R, Irimia M, Vignal E, Thibault P, Prinos P, Chabot B, Abou Elela S, Roux P, Lemaitre JM, Tazi J. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2480. Pubmed
- Targeting the Dbl and dock-family RhoGEFs: a yeast-based assay to identify cell-active inhibitors of Rho-controlled pathways. Blangy A, Fort P. Enzymes. 2013;33 Pt A:169-91. Pubmed
2012
- Tissue-specific alternative splicing of Tak1 is conserved in deuterostomes. Venables JP, Vignal E, Baghdiguian S, Fort P, Tazi J. Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Jan;29(1):261-9. Pubmed
- Fossil rhabdoviral sequences integrated into arthropod genomes: ontogeny, evolution, and potential functionality. Fort P, Albertini A, Van-Hua A, Berthomieu A, Roche S, Delsuc F, Pasteur N, Capy P, Gaudin Y, Weill M. Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Jan;29(1):381-90. Pubmed
- Novel AChE inhibitors for sustainable insecticide resistance management. Alout H, Labbé P, Berthomieu A, Djogbénou L, Leonetti JP, Fort P, Weill M. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47125. Pubmed
- Matrix-bound PAI-1 supports cell blebbing via RhoA/ROCK1 signaling. Cartier-Michaud A, Malo M, Charrière-Bertrand C, Gadea G, Anguille C, Supiramaniam A, Lesne A, Delaplace F, Hutzler G, Roux P, Lawrence DA, Barlovatz-Meimon G. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32204. Pubmed
- ZNF217 is a marker of poor prognosis in breast cancer that drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion. Vendrell JA, Thollet A, Nguyen NT, Ghayad SE, Vinot S, Bièche I, Grisard E, Josserand V, Coll JL, Roux P, Corbo L, Treilleux I, Rimokh R, Cohen PA. Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 15;72(14):3593-606. Pubmed
- Cooperative anti-invasive effect of Cdc42/Rac1 activation and ROCK inhibition in SW620 colorectal cancer cells with elevated blebbing activity. de Toledo M, Anguille C, Roger L, Roux P, Gadea G. PLoS One. 7(11):e48344. Pubmed
- Using a modified yeast two-hybrid system to screen for chemical GEF inhibitors. Blangy A, Fort P. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;928:81-95. Pubmed
2011
- Multiple Wolbachia determinants control the evolution of cytoplasmic incompatibilities in Culex pipiens mosquito populations. Atyame CM, Duron O, Tortosa P, Pasteur N, Fort P, Weill M. Mol Ecol. 2011 Jan;20(2):286-98. Pubmed
- MiniSOX9, a dominant-negative variant in colon cancer cells. Abdel-Samad R, Zalzali H, Rammah C, Giraud J, Naudin C, Dupasquier S, Poulat F, Boizet-Bonhoure B, Lumbroso S, Mouzat K, Bonnans C, Pignodel C, Raynaud P, Fort P, Quittau-Prévostel C, Blache P. Oncogene. 2011 Jun 2;30(22):2493-503. Pubmed
- Tara up-regulates E-cadherin transcription by binding to the Trio RhoGEF and inhibiting Rac signaling. Yano T, Yamazaki Y, Adachi M, Okawa K, Fort P, Uji M, Tsukita S, Tsukita S. J Cell Biol. 2011 Apr 18;193(2):319-32. Pubmed
- Activity of the RhoU/Wrch1 GTPase is critical for cranial neural crest cell migration. Fort P, Guémar L, Vignal E, Morin N, Notarnicola C, de Santa Barbara P, Faure S. Dev Biol. 350(2):451-63. Pubmed
2010
- What makes cells move: requirements and obstacles for spontaneous cell motility. Binamé F, Pawlak G, Roux P, Hibner U. Mol Biosyst. 6(4):648-61. Pubmed
- Gain of oncogenic function of p53 mutants regulates E-cadherin expression uncoupled from cell invasion in colon cancer cells. Roger L, Jullien L, Gire V, Roux P. J Cell Sci. 123(Pt 8):1295-305. Pubmed
2009
- TC10 controls human myofibril organization and is activated by the sarcomeric RhoGEF obscurin. Coisy-Quivy M, Touzet O, Bourret A, Hipskind RA, Mercier J, Fort P, Philips A. J Cell Sci. 2009 Apr 1;122(Pt 7):947-56. Pubmed
- A cell active chemical GEF inhibitor selectively targets the Trio/RhoG/Rac1 signaling pathway. Bouquier N, Vignal E, Charrasse S, Weill M, Schmidt S, Léonetti JP, Blangy A, Fort P. Chem Biol. 2009 Jun 26;16(6):657-66. Pubmed
2008
- Analysis of cell migration and its regulation by Rho GTPases and p53 in a three-dimensional environment. Vinot S, Anguille C, de Toledo M, Gadea G, Roux P. Methods Enzymol. 439:413-24. Pubmed
- Dynamic expression patterns of RhoV/Chp and RhoU/Wrch during chicken embryonic development. Notarnicola C, Le Guen L, Fort P, Faure S, de Santa Barbara P.Dev Dyn. 2008 Apr;237(4):1165-71. Pubmed
Équipe R&D : Migration, invasion et microenvironnement

Pierre ROUX
Chef d’équipe (Chercheur DR2 INSERM)
Membres de l’équipe
(CRCN) +33 (0)4 34 35 95 13 |
|
(Chercheur DR2) +33 (0)4 34 35 95 12 |
|
(IR-Recherche) +33 (0)4 34 35 95 12 |

Contactez notre équipe
Remplacez le nom et l’adresse ci-dessus par celui du membre à contacter
prenom.nom@crbm.cnrs.fr







